Understanding Viltnemnda: Norway’s Natural World Committee for Wildlife Management
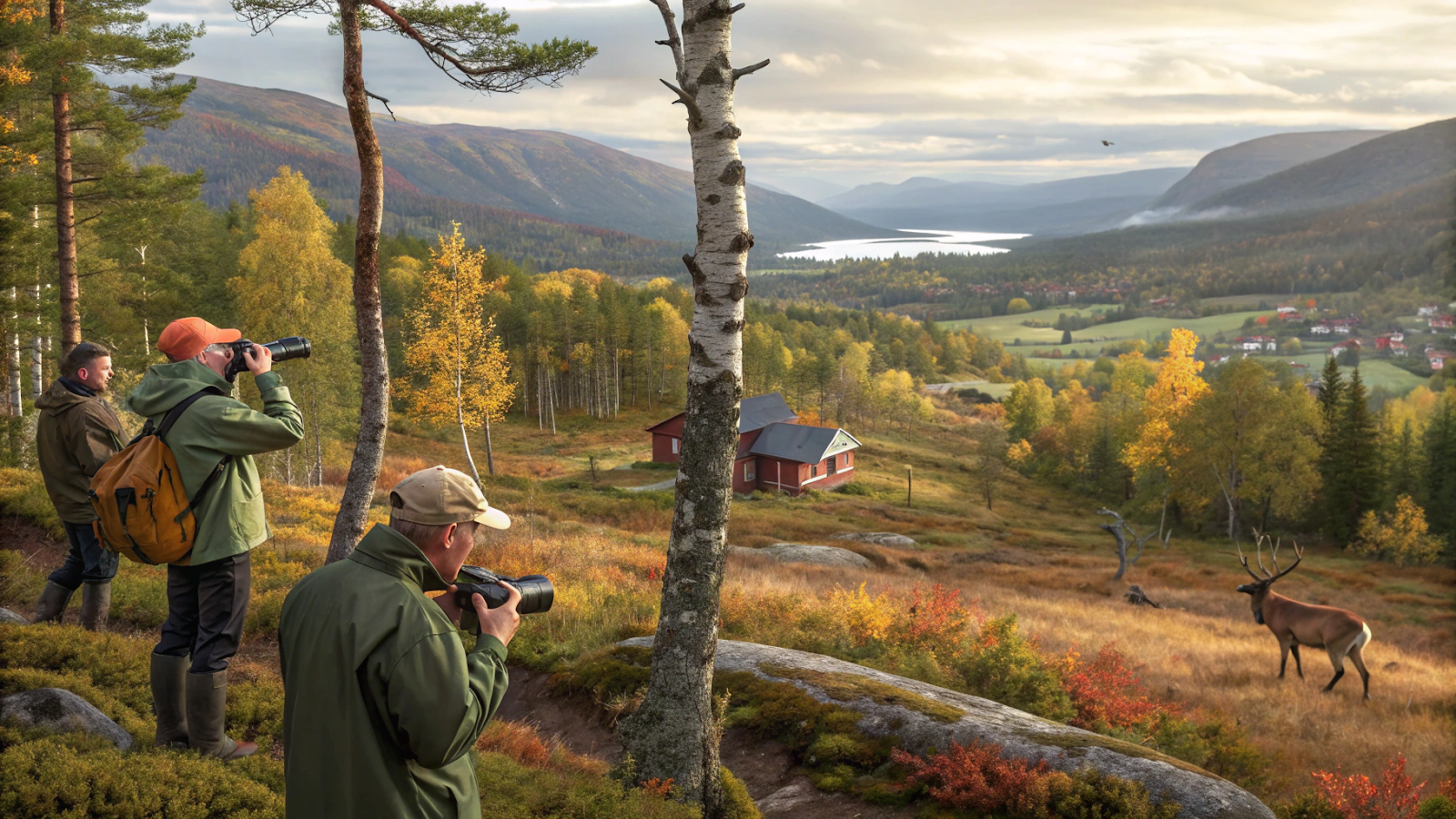
The term Viltnemnda, which literally means “natural world committee” in Norwegian, represents a crucial local government body dedicated to managing wildlife and ensuring a balanced coexistence between humans and nature. Let’s explore Viltnemnda’s role, responsibilities, and importance in protecting biodiversity, reducing conflicts, and promoting sustainable natural world practices in Norway.
What Is Viltnemnda?
Viltnemnda translates to “wildlife board” or “wildlife committee” in English. It is a municipal or local governing framework established by law in Norwegian municipalities to oversee wildlife management at the regional level. Each municipality has its own Viltnemnda, reflecting the unique ecological conditions and social aspects of the area.
The committee acts as the formal decision-making authority responsible for regulating hunting seasons and quotas, conservation measures, and resolving conflicts involving wild animals. Its creation empowers local stakeholders to contribute to the respectful management of Norway’s natural resources.
Structure and Key Responsibilities
Typically, Viltnemnda consists of local representatives with expertise in wildlife ecology, hunting, forestry, and community interests. By bridging national wildlife policies with grassroots action, the committee ensures that decisions are informed by both scientific knowledge and local realities.
The main responsibilities of Viltnemnda include:
- Setting hunting quotas and seasons: They regulate hunting licenses and limits to maintain healthy and sustainable wildlife populations.
- Managing protected areas and sensitive habitats: Viltnemnda oversees special zones to safeguard vulnerable species and preserve biodiversity hotspots.
- Resolving human-wildlife conflicts: This includes addressing issues like crop damage caused by animals or livestock predation.
- Promoting public awareness and education: Raising knowledge about wildlife conservation among hunters, farmers, and the general public.
- Coordinating with regional and national wildlife authorities: Ensuring that local decisions align with broader conservation goals and government regulations.
Importance of Viltnemnda to Local Communities
Viltnemnda holds a vital role in balancing economic, ecological, and cultural interests in Norwegian municipalities. Rural communities depend heavily on sustainable hunting and wildlife tourism as sources of income and cultural identity. By regulating these activities carefully, Viltnemnda supports both biodiversity conservation and local livelihoods.
Additionally, these committees help preserve traditional hunting practices, vital to Norway’s cultural heritage, while incorporating modern scientific insights into wildlife management. Open dialogue with hunters, farmers, conservation groups, and residents fosters collaboration and reduces potential disputes arising from wildlife interactions with human environments.
How Viltnemnda Influences Wildlife Conservation
Decisions made by Viltnemnda directly impact species protection and habitat preservation. The committees ensure hunting activities do not threaten wildlife populations or endangered species. Their work also contributes to reforestation efforts and biodiversity projects year-round.
Since Viltnemnda members possess intimate local knowledge, they design tailored strategies for different landscapes—whether coastal, forested, or mountainous—balancing ecological needs with human presence.
Challenges and the Evolving Role of Viltnemnda
The roles and responsibilities of Viltnemnda continue to evolve in response to growing environmental challenges. Climate change, habitat fragmentation, and increasing human development pressures demand adaptive wildlife management.
These committees face the delicate task of balancing economic priorities—such as agriculture, logging, and tourism—with ecological sustainability goals. Technology advancements like GPS tracking and data sharing have enhanced their ability to monitor wildlife and coordinate across various governance levels effectively.
However, keeping pace with fast-changing ecological conditions requires constant updates in management strategies, scientific understanding, and stakeholder engagement.
Conclusion: A Model Community-Based Wildlife Management
In summary, Viltnemnda represents Norway’s commitment to responsible, community-driven wildlife governance. By empowering local stakeholders to make informed decisions about wildlife and habitats, these committees play a crucial role in maintaining Norway’s environmental health, economic vitality, and cultural traditions.
This clear and accessible article provides readers with a meaningful understanding of Viltnemnda’s functions and relevance. It is particularly valuable for those interested in wildlife governance, conservation, and rural community dynamics.
Visit Magazineglow.net